Take-home points
|
 |
By the time you read this, the Food and Drug Administration may have already approved pegcetacoplan to be the first treatment for geographic atrophy secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Or not. One of the nuances about magazines is covering an event weeks or days before it happens.
In any event, 2023 is shaping up to be the year of GA, punctuated by the aforementioned pegcetacoplan (Apellis Pharmaceuticals). And in December 2022, Iveric Bio completed filing its New Drug Application for avacincaptad pegol, which may set the stage for FDA action this year.
This year’s listing consists of 87 investigative treatments either in or soon to be in clinical trials in six different categories:
- Neovascular age-related macular degeneration, diabetic macular edema, diabetic retinopathy and retinal vein occlusion.
- Geographic atrophy.
- Gene therapies for AMD, DR and DME.
- Biosimilars.
- Inherited retinal disorders.
- Devices.
The categories for GA treatments and devices are new. In all, this year’s list includes 87 entries, but not necessarily 87 different candidates; some of them are being investigated in different trials for different indications and are listed twice.
 |
Additions and subtractions
Some drugs are going by new names. Tarcocimab tedromer is the new name Kodiak Sciences has given to KSI-301. Tinlarebant is the name Belite Bio is using for LBS-008. And so on.
This year’s list includes 21 new entries, including six previously unlisted biosimilars and four each in treatments for inherited disorders and gene therapy candidates for nAMD, DME and DR.
2022 was known for significant approvals, namely Vabysmo (faricimab, Genentech/Roche) and Cimerli, Coherus Biosciences’ ranibizumab biosimilar. Also notable in the biosimilars space was Biogen’s launch of Byooviz, approved in 2021.
Clearside Biomedical and Bausch + Lomb also launched Xipere, the suprachoroidal triamcinolone acetonide suspension, for uveitic macular edema. It remains on the list because the sponsors are pursuing a program in DME.
Some candidates from last year’s list aren’t on this year’s. FHTR2163, also known as galegenimab or RG6147, was dropped because Roche reported last year that it would discontinue the program. Abicipar pegol was removed because Molecular Partners hasn’t issued any updates on the agent.
Biosimilar or not?
ONS-5010/Lytenava is listed in the large table for nAMD, DME, DR, RVO treatments rather than with biosimilars, although it’s actually a biosimilar of Avastin (bevacizumab, Genentech/Roche). The reason: if approved, it would be the first ophthalmic formulation of bevacizumab, whereas the reference product is prepared by specialty pharmacies from batches of the cancer drug. The FDA set an action date for August.
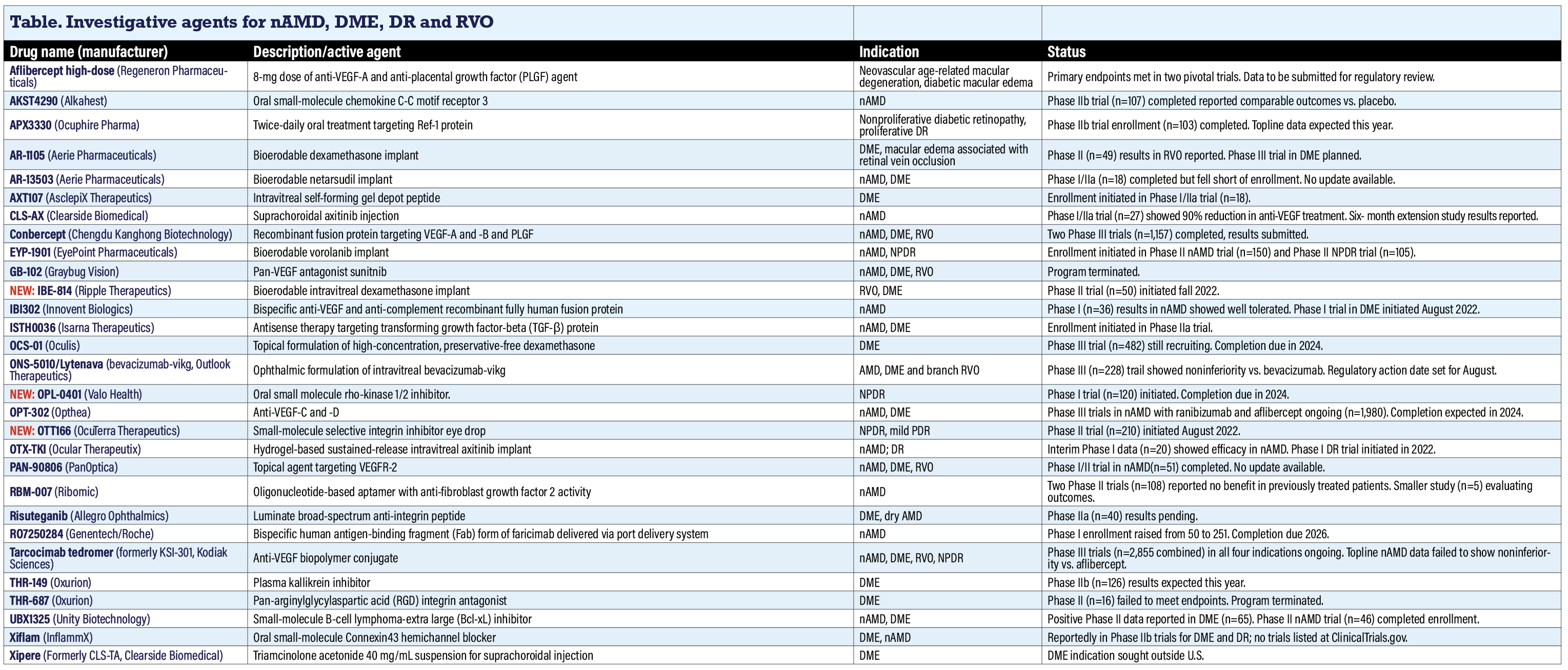
Investigative agents for nAMD, DME, DR and RVO
Aflibercept high-dose (Regeneron Pharmaceuticals)
Two pivotal trials of this novel 8-mg aflibercept formulation, known as high-dose aflibercept (the 2-mg aflibercept is branded as Eylea), met their primary endpoints. The PHOTON trial in diabetic macular edema and PULSAR trial in neovascular age-related macular degeneration both demonstrated that aflibercept 8 mg 12- and 16-week dosing regimens achieved noninferiority in vision gains compared to aflibercept 2 mg 8-week dosing. Regeneron and Bayer, which holds the aflibercept franchise outside the United States, say they’ll submit these data for regulatory review.
AKST4290 (Alkahest)
AKST4290 is an oral inhibitor of the chemokine C-C motif receptor 3 (CCR3) that blocks action eotaxin, an immunomodulatory protein that increases as humans age and contributes to age-related diseases. The Phase IIb PHTHALO-205 trial (n=107, NCT04331730), completed in 2021, randomized patients to either 800 or 1,600 mg of AKST4290 daily or placebo. All participants also received unspecified aflibercept injections. The trial is evaluating visual acuity outcomes after three loading doses of aflibercept in treatment-naive nAMD patients. Placebo patients actually had a more robust improvement in best-corrected visual acuity; 41.7 percent had a >15-letter improvement after 36 weeks vs. 30.6 and 14.3 percent in the low- and high-dose AKST treatment groups. Change in central subfield thickness and time to first aflibercept injection (about 20 weeks) were also comparable across the treatment arms. Alkahest didn’t respond to a query for updated information.
APX3330 (Ocuphire Pharma)
Ocuphire reported its Phase II ZETA-1 trial (n=103, NCT04692688) in patients with moderately severe-to-severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy or mild proliferative diabetic retinopathy failed to meet its primary endpoint, but met systemic and ocular safety endpoints. The company reports it’s preparing for an end-of-Phase II meeting with the FDA.
 |
| Click image to enlarge. |
AR-1105, AR-13503 (Aerie Pharmaceuticals)
AR-1105 is a dexamethasone implant platform for DME and retinal vein occlusion. An open-label six-month study (n=49, NCT03739593) in patients with macular edema due to RVO demonstrated improvements in BCVA. Preparations for Phase III trials in DME are underway.
AR-13503 is a rho-kinase inhibitor implant that’s an active metabolite of netarsudil. In preclinical studies, AR-13503 demonstrated efficacy as a monotherapy and anti-VEGF adjunct. It’s also the subject of a Phase I study in nAMD and DME (n=18, NCT03835884).
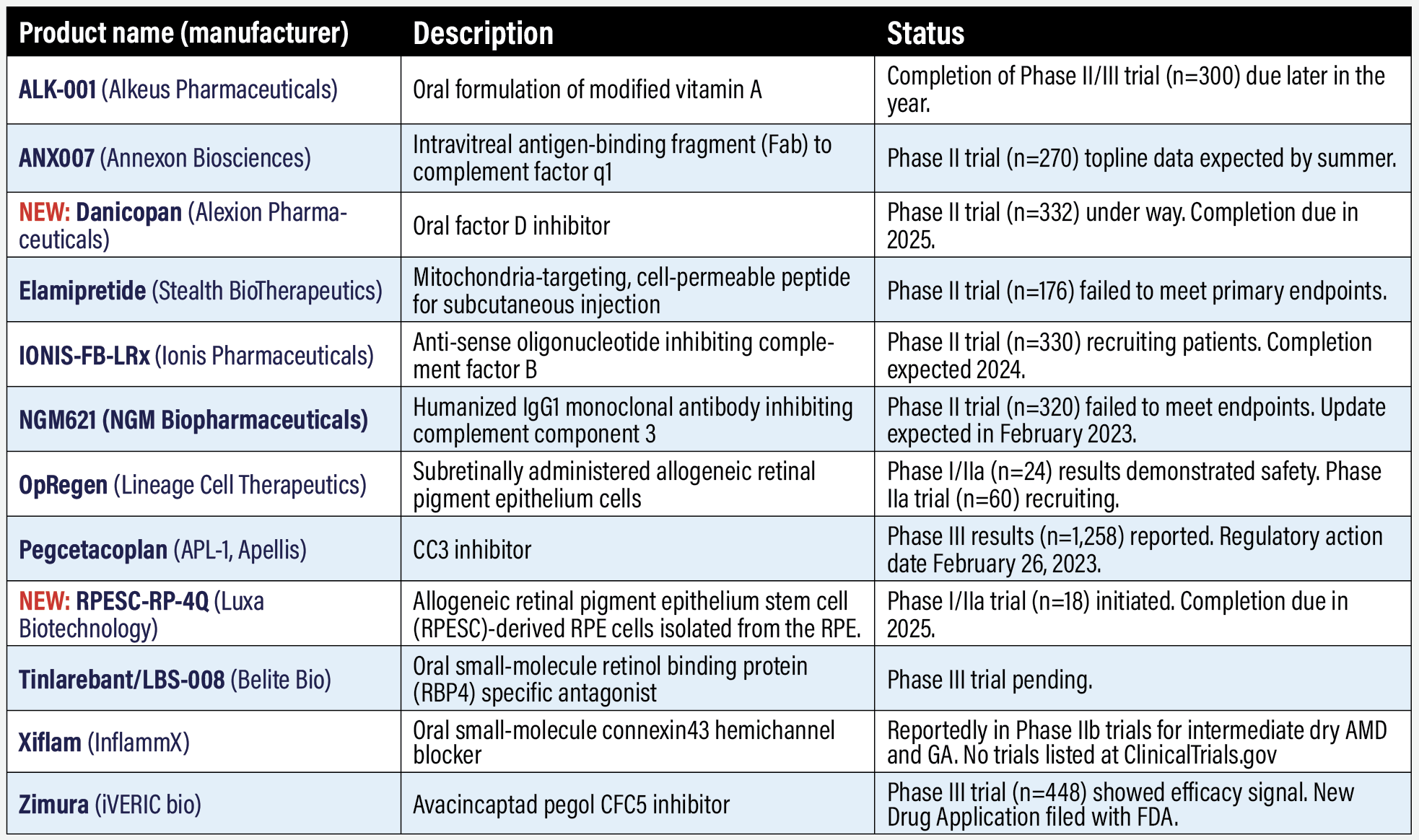
Investigative programs in geographic atrophy ALK-001 (Alkeus Pharmaceuticals) Recruiting ended in 2021 in a Phase II/III trial (n=300, NCT03845582) of this oral modified form of vitamin A, but results still haven’t been posted. ALK-001 aims to replace the body’s natural vitamin A with a form that makes vitamin A dimers more slowly and prevents toxic vitamin A dimer formation. The geographic atrophy study is due for completion later in the year. Alkeus is also pursuing concurrent trials in Stargardt disease. Alkeus didn’t reply to a query for an update. ANX007 (Annexon Biosciences) Annexon completed patient enrollment in the Phase II ARCHER trial evaluating this anticomplement factor 1q candidate (n=270, NCT NCT04656561). Annexon says it plans to report topline data on the primary endpoint in the first half of 2023, following 12 months of treatment, with full data expected after conclusion of a six-month off-treatment period. Study completion is set for the end of the year. NEW: Danicopan (Alexion Pharmaceuticals) Also known as ALXN2040, Danicopan is an oral factor D inhibitor that’s also being investigated as an add-on therapy in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. A Phase II trial (n=332, NCT05019521) is evaluating danicopan as a monotherapy for GA. The trial started late in 2021 and is due for completion in 2025. Elamipretide (Stealth BioTherapeutics) The Phase II ReCLAIM-2 study of this cell-permeating peptide (n=176, NCT03891875) failed to meet its primary endpoints—change in low-luminance visual acuity (LLVA) and GA lesion size. But the latest data demonstrated >2-line improvement in LLVA in study participants, results that were promising enough to continue the program, according to Stealth. Elamipretide was generally well tolerated in study participants. The rate of new-onset exudations was 5.3 percent in the elamipretide arm vs. 6.9 percent for placebo. IONIS-FB-LRx (Ionis Pharmaceuticals/Roche) The Phase II GOLDEN study for GA (n=330, NCT03815825) is still recruiting. The primary endpoint is change in GA area at week 49. Secondary outcomes measure key biomarkers: levels of factor B in plasma and serum AH50 activity, as well as LLVA. Study completion has been pushed back to early next year. IONIS-FB-LRx is an antisense inhibitor. NGM621 (NGM Biopharmaceuticals) NGM Biopharmaceuticals is sorting through CATALINA Phase II trial results (n=320, NTC04465955) to determine next steps for this monoclonal antibody that aims to inhibit complement component 3 (C3) activity. The trial failed to meet its primary endpoint: A statistically significant reduction in GA lesion area vs. sham over 52 weeks. A post hoc analysis showed a subgroup had a more robust response than the overall study population.1 This subgroup had a narrower range of GA lesion area than the trial inclusion criteria— 4.17 to 9.64 mm2 vs. ≥2.5 mm2 and ≤17.5 mm2. In this subgroup, NGM621 demonstrated a reduction in the rate of change in GA lesion area (slope) of 21.9 percent (q4 weeks) (n=55) and 16.8 percent (q 8 weeks) (n=52), compared to sham (n=53). Updated CATALINA results are due soon. OpRegen (Lineage Cell Therapeutics) This cell-transplant platform consists of allogeneic retinal pigment epithelium cells delivered subretinally. One-year post-transplant results in the ongoing Phase I/IIa trial (NCT02286089) showed that all 24 treated patients reported at least one adverse event (AE) and at least one ocular AE, but around 90 percent of AEs in the first four cohorts were mild in nature. No cases of rejection, acute or delayed intraocular inflammation, or sustained increases in intraocular pressure were reported. A Phase IIa, multicenter, open-label, single-arm clinical study (n=60, NCT05626114) is recruiting. Genentech/Roche has partnered with Lineage to develop OpRegen. Pegcetacoplan (Apellis Pharmaceuticals) Anticipation was building last year when the Food and Drug Administration set a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) target action date of November on Apellis’ New Drug Application (NDA) for pegcetacoplan. But then Apellis pulled the application back so it could resubmit it with updated 24-month data from the Phase III Phase III DERBY (n=621, NCT03525600) and OAKS studies (n=637, NCT03525613). With the amended NDA filed, the FDA set a new PDUFA action date of February 26. The 24-month data showed that patients on monthly and bimonthly therapy lost mean threshold sensitivity at a slower rate than sham and had significantly fewer scotomatous points than sham patients.1,2 Apellis last year also submitted a Marketing Authorization Application to the European Medicines Agency. Pegcetacoplan targets C3. NEW: RPESC-RPE-4Q (Luxa Biotechnology) RPESC-RPE-4W consists of allogeneic retinal pigment epithelium stem cell (RPESC)-derived RPE cells isolated from the RPE layer of human cadaveric eyes, transplanted under the macula. The first patient received the cell product transplant in the Phase I/IIa clinical trial last spring (n=18, NCT04627428). The trial is evaluating the safety, tolerability, feasibility and preliminary efficacy of subretinal RPESC-RPE-4W using a dose-escalation, open-label design. Study completion is due in May 2025. Luxa is a joint venture of Seoul-based Y2 Solution Co. and the Neural Stem Cell Institute, Rensselaer, New York. Tinlarebant/LBS-008 (Belite Bio) Belite Bio says it has finalized design of its Phase III clinical trial in GA, but the study hasn’t been filed with ClinicalTrials.gov yet. Tinlarebant is an oral, small-molecule retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) specific antagonist. A previous Phase I trial (n=71, NCT03735810) confirmed safety and tolerability of the drug and that oral administration achieved a potentially therapeutic level of the agent. A Phase III trial in Stargardt disease is ongoing. Xiflam (InflammX) InflammX said last fall that it planned to initiate by year end separate Phase IIb clinical trials in intermediate dry AMD and GA, but no trials are registered at ClinicalTrials.gov. It submitted an Investigational New Drug amendment last year that it said would allow the DRCR Retina Network to initiate a Phase IIb trial in DME as well as diabetic nephropathy. Zimura/ avacincaptad pegol (Iveric Bio) Avacincaptad pegol (ACP), a complement C5 inhibitor, appears to be next GA treatment in the queue for approval and commercialization. Last fall the FDA granted Breakthrough Therapy designation to ACP for GA. In December Iveric Bio filed with the FDA the third and final installment of its NDA. The submission is based on 12-month results from the Phase II/III GATHER1 (n=286, NCT02686658) and Phase III GATHER2 (n=448, NCT04435366) clinical trials. Both trials randomized patients to either ACP 2 mg or sham monthly. Topline data from GATHER2 showed treated patients had a 14.3-percent reduction in the average rate of GA area growth over 12 months (p=0.0064).3 An update from the Phase III GATHER 2 trial is due in February. An extension study is following patients who completed GATHER2 with monthly ACP 2 mg for up to 18 months (n=400, NCT055326297). ACP is also the subject of a clinical trial in Stargardt disease.
REFERENCES 1. Wykoff CC. Safety and efficacy of NGM621, a monoclonal antibody against C3 for treatment of geographc atrophy: Results from the Phase II CATALINA study. Paper presented at the 55th annual meeting of The Retina Society; Pasadena, CA; November 3, 2022. 2. Wykoff CC. Treatment of geographic atrophy secondary to AMD with pegectacoplan: Two-year outcomes from the randomized Phase III DERBY and OAKS trials. Paper presented at the American Academy of Ophthalmology Retina Subspescialty Day; Chicago, IL; September 30, 2022. 3. Khanani AM. GATHER2 pivotal Phase III study results: Efficacy of intravitreal avacincaptad pegol in geographic atrophy. Paper presented at the American Academy of Ophthalmology Retina Subspecialty Day; Chicago, IL; September 30, 2022. |
AXT107 (AsclepiX Therapeutics)
AsclepiX last year completed a small Phase I/IIa trial in DME (n=6, NCT04697758), but hasn’t reported any results. AXT107 aims to inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor A and C and activate the Tie2 pathway as well. Enrollment fell short of the previously stated goal of 18. The company didn’t respond to a request for further information by press time.
CLS-AX (Clearside Biomedical)
This injectable suspension of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) axitinib is administered suprachoroidally via Clearside’s SCS Microinjector platform. Clearside recently reported what it characterized as positive results from the Phase I/IIa OASIS extension study (n=19, NCT05131646) in nAMD.
In the extension study, 67 percent of participants went at least six months without needing additional treatments. They also had a 77 to 85 percent reduction in treatment burden over six months.
The OASIS Phase I/IIa study itself (n=27, NCT04626128) demonstrated that observable signs of the potential biologic effect of suprachoroidal axitinib included stable average BCVA and stable average central subfield thickness, which the extension study confirmed.
Conbercept (Chengdu Kanghong Biotechnology)
Chengdu Kanghong’s plans last year to get FDA approval for the anti-VEGF fusion protein conbercept fell through. Available in China since 2013, conbercept targets VEGF-A and -B along with placental growth factor. Results from two Phase III trials in nAMD, PANDA-1 and PANDA-2 (NCT03577899; NCT03630952), each enrolling 1,157 patients, were submitted earlier this year. They’re now listed as terminated. Small, independent studies were published last year in RVO.1,2 Multiple studies in China are evaluating conbercept for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy, retinoblastoma and other ophthalmic indications.
EYP-1901 (EyePoint Pharmaceuticals)
EYP-1901 is a bioerodable sustained release insert that uses the Durasert platform with the TKI vorolanib. Last year enrollment commenced for the Phase II DAVIO 2 (Durasert and Vorolanib in Ophthalmology 2) trial in nAMD (n=150, NCT05381948). Topline data are expected in the fourth quarter this year and the trial is expected to enroll patients previously treated with anti-VEGF therapy.
Enrollment also started in the Phase II PAVIA trial in NPDR (n=105, NCT05383209). Completion is due in 2025.
GB-102 (Graybug Vision)
Graybug terminated development of this sustained-release, bioerodible platform using the TKI sunitinib. Graybug entered into a merger agreement with CalciMedica with a plan to focus on development of a drug for treating acute pancreatitis.
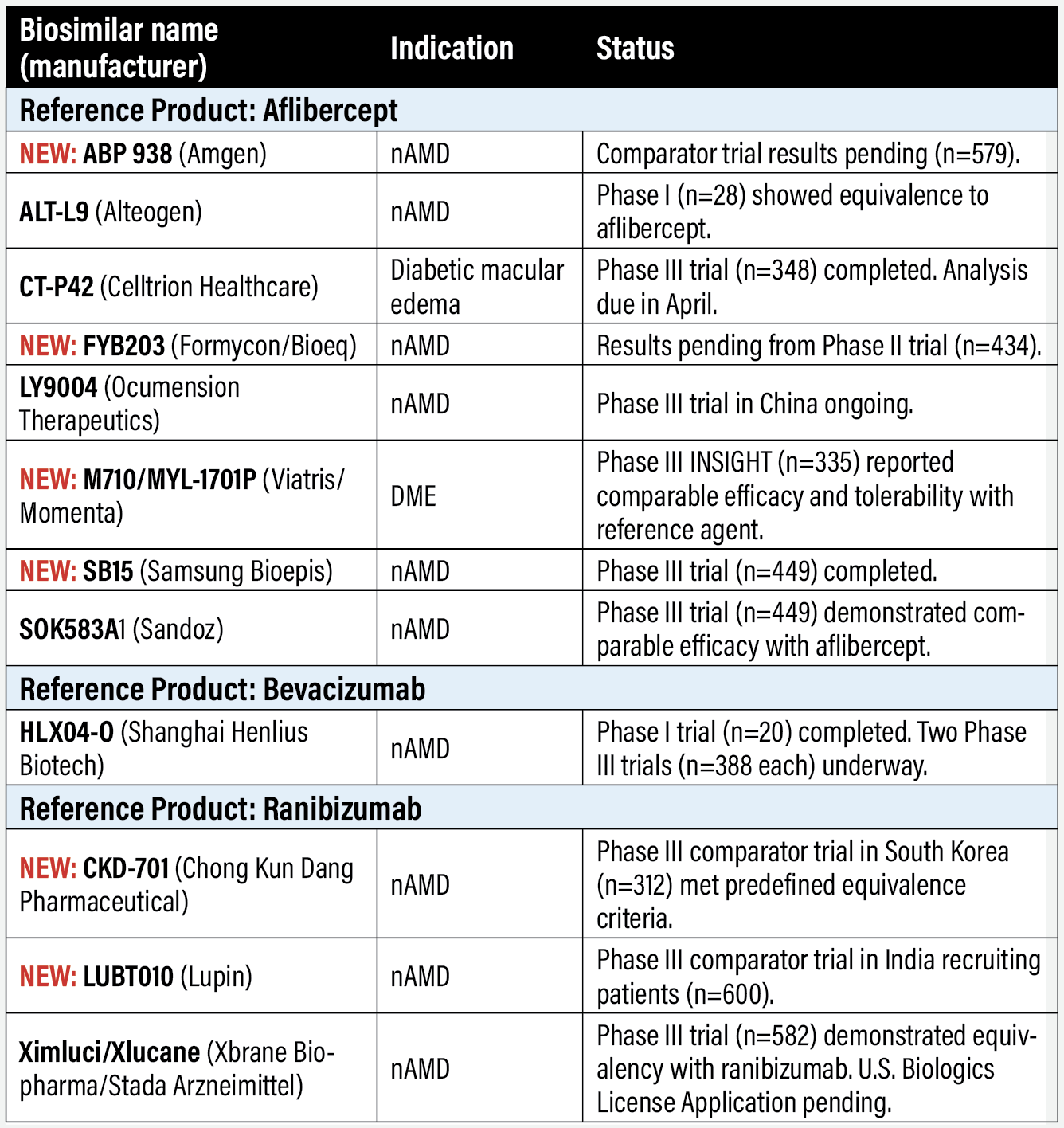
Anti-VEGF biosimilars in clinical trials Aflibercept biosimilars NEW: ABP 938 (Amgen) Results are pending from a comparator trial with aflibercept in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (n=579, NCT04270747). Primary outcome is change in best-corrected visual acuity at eight weeks. Amgen reported in November 2022 that data were expected by year end, but none have been reported as of press time. ALT-L9 (Alteogen) South Korea-based Alteogen reported in January that it completed a Phase I trial in its home country of ALT-L9 in nAMD. ALT-L9 showed similar safety and efficacy to the reference product. The results will aid in the design of a Phase III trial. In 2021, Alteogen completed an earlier Phase I comparator trial (n=28, NCT-04058535) that showed equivalent efficacy in nAMD. CT-P42 (Celltrion) Celltrion concluded enrollment in a Phase III trial in diabetic macular edema (n=348, NCT04739306). Completion of the analysis is set for April. NEW: FYB203 (Formycon/Bioeq) Enrollment in the Phase III MAGELLAN-AMD trial in nAMD ended last year with results pending (n=434, NCT04522167). Primary outcome is change in BCVA at eight weeks. A sale of U.S. rights to Coherus BioSciences is pending. LY9004 (Ocumension Therapeutics/Shandong Boan Biological Technology) Luye Pharma’s biotech subsidiary Boan Biological licensed LY9004, also known as OT-702, to China-based Ocumension. The asset is in Phase III trials for nAMD in China, but not in the United States. Boan holds licensing rights outside China. NEW: M710/MYL-1701P (Viatris/Momenta) One-year results of trial in people with central DME (n=355, NCT03610646) demonstrated therapeutic equivalence with the reference product.1 In the MYL-1701P vs. Eylea arms, the proportion of eyes that gained ≥15 and ≥10 letters were 32.4 vs. 29.3 percent and 57.4 vs. 58 percent, respectively. The proportions for ≥5- and ≥10-letter losses were 3.4 vs. 4 percent and 1.7 vs. 1.7 percent. Results are pending from an extension study evaluating the safety and efficacy (n=52, NCT04674800). NEW: SB15 (Samsung Bioepis) A Phase III comparator trial with aflibercept in nAMD was completed last year (n=449, NCT04450329). It met the primary endpoint: comparable change from baseline in BCVA at week 8. A 32-week interim analysis also demonstrated comparability in other secondary efficacy endpoints, safety, immunogenicity and pharmacokinetics. SOK583A1 (Sandoz) Sandoz, a division of Novartis, closed patient enrollment in the Phase III MYLIGHT trial (n=85, NCT04864834) in nAMD comparing SOK583A1 with the reference product. The trial is evaluating change in BCVA after 52 weeks.
Bevacizumab biosimilar HLX04-O (Shanghai Henlius Biotech) SHB is enrolling patients in two Phase III studies in nAMD: one in Australia (n=388, NCT04740671) and the other in China (n=388, NCT05003245), with completion dates of June this year and March 2024, respectively. A Phase I safety and efficacy trial in China reported HLX04-O was well tolerated (n=20, NCT04993352).3 The biosimilar is already approved in China for cancer indications.
Ranibizumab biosimilars NEW: CKD-701 (Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical) A Phase III clinical trial in nAMD with ranibizumab as the comparator has found the biosimilar met predefined equivalence criteria (n=312, NCT04857177).4 The trial was conducted in South Korea, where the sponsor company is located. Chong Kun Dang has a host of affiliations with U.S. companies, including Pfizer and Amgen. NEW: LUBT010 (Lupin) A Phase III comparator trial with the reference product in nAMD is recruiting patients in India (n=600, NCT04690556). The primary endpoint is change in BCVA at 12 months. Lupin has received Food and Drug Administration approval for a host of generic medications and has two oncology biosimilars—one for Filgrastim, for which it has filed for FDA approval, and the other for Etanercept, which is approved in India, Japan and the European Union. Ximluci/Xlucane (Xbrane Biopharma/Stada Arzneimittel) The European Commission granted marketing authorization last fall for what was known as Xlucane and the United Kingdom followed up with approval in January. Launch is set in both markets for early this year. In the United States, Xbrane and Stada withdrew the Biologics License Application it filed with the FDA, postponing that regulatory step to the first quarter of this year. The sponsors last spring completed a Phase III trial (n=582, NCT03805100), which demonstrated equivalency with the reference product. Bausch + Lomb has an agreement with Xbrane and Stada to commercialize Ximluci in the United States and Canada.
REFERENCES 1. Bressler SB, Barve A, Beckmann K, et al. MYL-1701P (proposed biosimilar aflibercept) compared to Eyelea in DME: Outcomes from the Phase 3 INSIGHT Study. Poster PO387. Presented at American Academy of Ophthalmology. 2. Woo SJ, Saddam SRm Bradvica M, et al. A proposed biosimilar to aflibercept in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD): 31-week results. Poster PO381. Presented at American Academy of Ophthalmology. 3. Zhang Z, Wu Y, Lyu YL, et al. Efficacy and safety of intravitreal HLX04-O, an anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of wet age-related macular degeneration. Int J Ophthalmol. 2022;15:1549-1553. 4. Yoon CK, Oh J, Bae K, Park UC, Yu KS, Yu HG. Efficacy and safety of a new ranibizumab biosimilar CKD-701 using a pro re nata treatment regimen in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: A Phase 3 randomized clinical trial. PLoS One. 2022;17:e0275611. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275611. |
NEW: IBE-814 (Ripple Therapeutics)
This is a bioerodible, intravitreal implant that, according to Ripple Therapeutics, releases one-tenth the drug load of the corticosteroid dexamethasone. A Phase II trial in RVO and DME launched last fall (n=50, NCT04576689). The company reports that trials so far haven’t shown the increase in intraocular inflammation that comes with other corticosteroids in the eye.
IBI302 (Innovent Biologics)
IBI302 (efdamrofusp alfa) is an intravitreal bispecific antibody that targets both VEGF and C3b/C4b pathways. Preliminary results from the Phase I dose-escalation trial in nAMD (n=36, NCT03814291) showed it was well tolerated.3
Preclinical studies showed the bispecific fusion protein demonstrated superior efficacy over anti-VEGF monotherapy. The dual-inhibition action was found to further inhibit macrophage infiltration and M2 macrophage polarization.3
ISTH0036 (Isarna Therapeutics)
ISTH0036 targets the transforming growth factor-ß (TGF-ß). Isarna initiated enrollment in 2021 in BETTER, a Phase IIa trial evaluating this antisense therapy in nAMD and DME (the trial isn’t listed at ClinicalTrials.gov). Results from 18 treated patients enrolled so far demonstrated an acceptable safety profile out to 12 months, with no drug-related adverse events and no signs of ocular inflammation.4
The study aims to enroll as many as 30 patients for each indication and is being conducted in Austria and India. The primary endpoint is retinal fluid and central macular thickness reduction, with improvement of BCVA as a secondary endpoint. The trial aims to explore the prevention of fibrosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition as a key differentiator to anti-VEGF therapies.
OCS-01 (Oculis)
OCS-01 is a topical formulation of high-concentration, preservative-free dexamethasone. The Phase III DIAMOND trial (n=482, NCT05066997) in DME is listed as recruiting, but no updates have been posted since 2021. The trial is due for completion in 2024.
ONS-5010/Lytenava (bevacizumab-vikg, Outlook Therapeutics)
ONS-5010 is an ophthalmic formulation of Avastin. Outlook lived up to its word to file a Biologics License Application (BLA) with the FDA for ONS-0510, which the agency accepted last fall. The FDA set a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) date for action by August 29 this year. The application was based on results from the Phase III NORSE TWO trial (n=228, NCT03834753) in nAMD which showed noninferiority vs. ranibizumab.
NEW: OPL-0401 (Valo Health)
Valo Health initiated a Phase II multicenter study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of oral OPL-0401 in patients with mild, moderate and severe NPDR (n=120, NCT05393284). OPL-0401 is a small molecule rho-kinase 1/2 inhibitor. Trial completion is set for 2024.
OPT-302 (Opthea)
Two Phase III trials in nAMD are ongoing: ShORe (n=990, NCT04757610) and COAST (n=990, NCT04757636). They’re evaluating intravitreal 2-mg OPT-302 in combination with 0.5 mg ranibizumab or 2 mg aflibercept, respectively. Study completion is set for the end of next year. Opthea says it expects to report topline 52-week results later in the year.
Phase IIb data of OPT-302 in combination with ranibizumab for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy demonstrated a safety profile that was consistent with standard-of-care anti-VEGF-A monotherapy.5
The study also reportedly demonstrated greater improvements in BCVA and less retinal fluid in OPT-302-treated patients than in those on ranibizumab monotherapy at week 24.
NEW: OTT166 (OcuTerra Therapeutics)
Patient enrollment started in the Phase II DR:EAM trial (it stands for Diabetic Retinopathy: Early Active Management) evaluating OTT166 in adults with moderately severe to severe NPDR or mild PDR with minimal vision loss (n=210, NCT05409235). OTT166 is a small-molecule, selective integrin inhibitor eye drop application. OTT166 is designed to be used as an eye drop by the patient at home before DR advances to a vision-threatening stage.
OTX-TKI (Ocular Therapeutix)
Ten-month interim data from the Phase I trial (n=21, NCT04989699) of this intravitreal axitinib implant for nAMD is due in February. Interim seven-month data showed 73 percent of treated patients were rescue-free and had outcomes for change in BCVA and change in central subfield thickness comparable to the aflibercept arm.6 The company also says it initiated a Phase I trial in DR, but that hasn’t been registered with ClinicalTrials.gov.
PAN-90806 (PanOptica)
This topical formulation is a selective inhibitor of VEGF receptor 2. The Phase I/II trial in nAMD has been completed (n=51, NCT03479372), but no updates have been issued. PanOptica didn’t respond to an inquiry by press time.
RBM-007 (Ribomic)
Two Phase II studies evaluating RBM-007, an anti-fibroblast growth factor-2 aptamer, for nAMD have shown no benefit of either monotherapy or combination treatment with aflibercept in previously treated patients (TOFU, n=86, NCT04200248; and RAMEN, n=22, NCT04640272).
However, Ribomic says that data from the much smaller TEMPURA IST study (n=5, NCT04895293) demonstrated what it characterized as “a positive trend” for improvement in BCVA and central subfield thickness. Most study participants also reportedly showed improvement in the two endpoints.
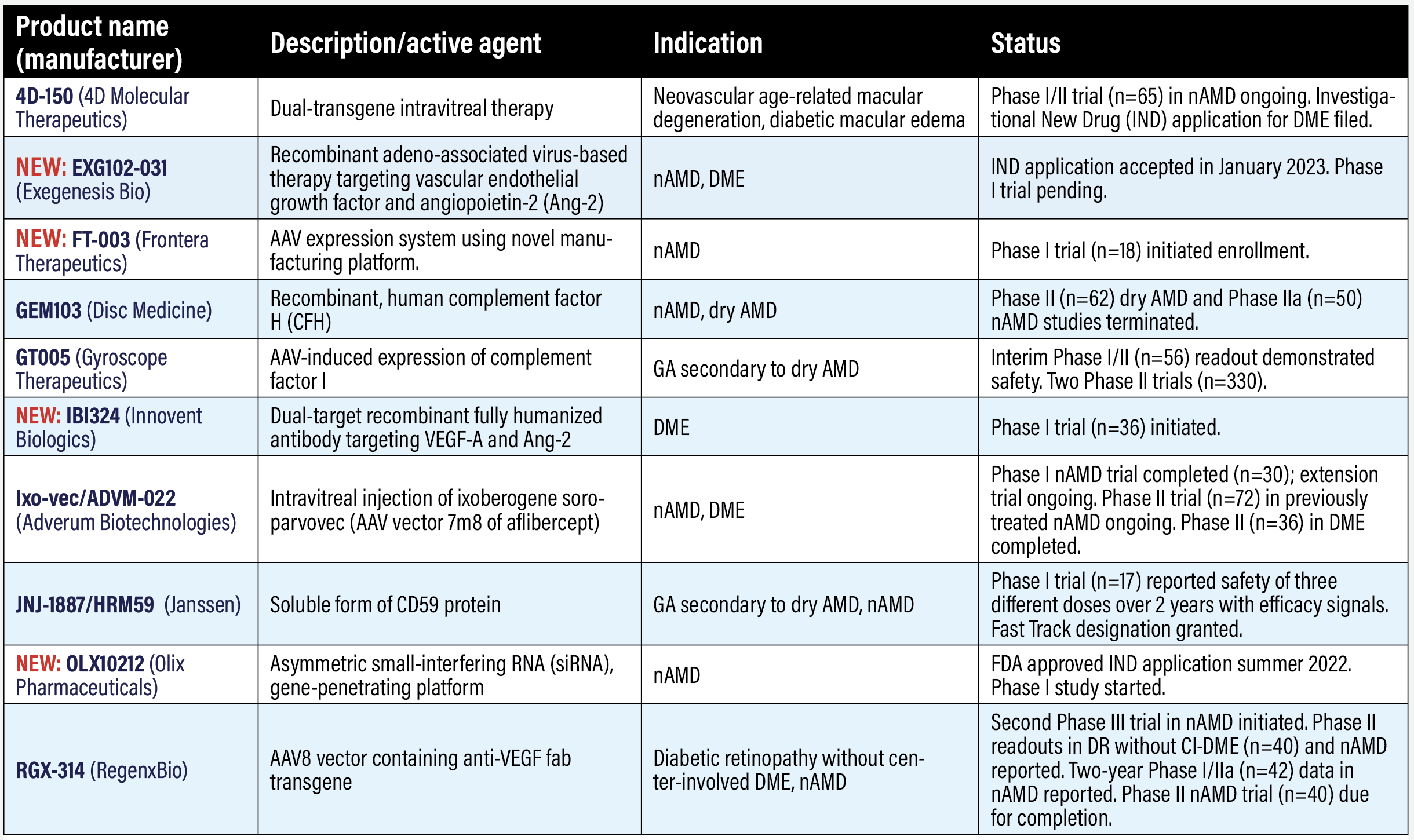
Gene therapy trials in AMD, DR, DME 4D-150 (4D Molecular Therapeutics) 4D-150 consists of the targeted and evolved intravitreal vector, R100, and a payload that expresses aflibercept and a vascular endothelial growth factor-C RNA interference. The dual transgene payload inhibits VEGF-A, B, C and placental growth factor. A Phase I/II trial in neovascular age-related macular degeneration started in 2021 (n=65, NCT05197270). Interim clinical data from the first cohort (n=5) demonstrated the treatment was safe and well tolerated. A subset of three patients had mediated expression of the aflibercept transgene protein in the aqueous humor 12 weeks after injection. The cohort patients’ annualized anti-VEGF injection rates were reduced by 96.7 percent. The study is due for completion in 2026. 4DMT also filed an Investigational New Drug (IND) application for a trial in diabetic macular edema, which the company says it expects to initiate later in 2023. NEW: EXG102-031 (Exegenesis Bio) The Food and Drug Administration has cleared the IND application for EXG102-031, a recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV)-based gene therapy delivered via intraocular injection that aims to express a therapeutic fusion protein that binds or neutralizes all known subtypes of VEGF and angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2). NEW: FT-003 (Frontera Therapeutics) Frontera just dosed the first patient in a Phase I trial in nAMD in China (n=18, NCT05611424). Frontera describes FT-003 as a AAV gene-expression system using its proprietary APEX manufacturing platform. GEM103 (Disc Medicine) Gemini Therapeutics, acquired last year by Disc Medicine, developed GEM103, a recombinant human complement factor H (CFH) protein, but terminated Phase II studies in both nAMD and (n=50, NCT04684394) and dry AMD (n=62, NCT04643886). Both studies showed the therapy was well tolerated. The dry AMD trial showed GEM103 could reduce complement activation biomarkers while maintaining supraphysiological levels of CFH. GT005 (Gyroscope Therapeutics/Novartis) GT005 aims to induce expression of complement factor I. Interim data from the Phase I/II FOCUS trial in geographic atrophy (n=56, NCT03846193) showed the treatment was well tolerated.2 FOCUS evaluated two delivery methods: transvitreal subretinal injection and with the Orbit subretinal delivery system (SDS). Of the eight patients who had the SDS treatment, six had 20 ocular adverse events, all considered mild and unrelated to treatment. Three other trials of GT005 in nAMD are underway: ORACLE, a long-term follow-up evaluating safety and durability (n=200, NCT05481827), with completion due in 2028; EXPLORE, a Phase II trial of two doses in GA (n=75, NCT04437368), with completion due in 2025; and HORIZON, a Phase II trial of medium- and high-dose therapy in GA (n=255, NCT04566445), with completion due in 2025. Novartis acquired Gyroscope last year. NEW: IBI324 (Innovent Biologics) Innovent describes IBI324 as an intravitreal, dual-target specific fully humanized antibody that targets VEGF-A and Ang-2. The first patient was dosed in the Phase I trial in DME (n=21, NCT05489718). Ixo-vec/ADVM-022 (Adverum Biotechnologies) Adverum reported two-year results from the Phase I OPTIC trial in nAMD of what it now calls Ixo-vec—for ixoberogene soroparvovec— (n=30, NCT03748784).1 The trial evaluated two different doses: a 2 x 1011 vector genes per eye (vg/eye) and a lower 6 x 1011 vg/eye dose. Ixo-vec seemed to be well tolerated and dose-dependent inflammation responded to steroids. All higher-dose patients were inflammation and steroid-treatment free at study conclusion. Annualized anti-VEGF injections declined 81 to 98 percent and aflibercept protein levels were sustained through three years in the extension study. Fifty-three and 80 percent of the 2E11 and 6E11 dose groups, respectively, were supplemental injection free over two years. All 30 OPTIC participants are enrolled in the OPTIC extension trial (NCT04645212), with completion set for June 2025. The first patient was dosed in the in the Phase II LUNA trial (n=72, NCT05536973), which is evaluating both doses in previously treated nAMD. Completion is set for this year. Adverum also registered a Phase II trial for both doses in DME (n=36, NCT04418427), which ended in December 2022. Results are pending. JNJ-1887/HRM59 (Janssen Pharmaceuticals) JNJ-1887 is an intravitreal treatment that aims to increase expression of a soluble form of CD59 (sCD59) to protect retinal cells. Originally developed by Hemera Biosciences, Janssen, a Johnson & Johnson company, acquired the rights last year to what was known as HRM59 (it’s also called JNJ-81201887 and formerly AAVCAGsCD59). A readout of a Phase I dose-escalation study of a single intravitreal injection (n=17, NCT03144999) reported that patients were treated at three escalating doses without steroid prophylaxis, meeting its primary endpoint of safety and tolerability, warranting further investigation.3 The FDA granted JNJ-1887 Fast Track designation. NEW: OLX10212 (Olix Pharmaceuticals) The FDA approved an IND application for this agent that uses an asymmetric small-interfering RNA (siRNA), gene-penetrating technology to target genetic origins of inflammation. The Phase I trial (n=60, NCT05643118) started recruiting patients in December 2022. RGX-314 (RegenxBio) This AAV-8 vector contains an anti-VEGF transgene delivered suprachoroidally. Early results of the Phase II AAVIATE trial in nAMD (n=115, NCT04514653) showed 85 patients in the first five cohorts tolerated the suprachoroidal delivery well.4 Patients in the RGX-314 arms received 2.5 x 1011 or 5 x 1011 genomic copies per eye (gc/eye) dose. They continued to demonstrate stable BCVA and central retinal thickness at six months, as did the ranibizumab control arm. More than 70 percent of patients needed fewer anti-VEGF injections after treatment. Ten of 15, or 67 percent, in the third dose level needed no anti-VEGF injections over six months after administration. RegenxBio says the Phase II/III ATMOSPHERE (n=300, NCT04704921) and ASCENT (n=465, NCT05407636) trials, scheduled for completion in 2023, are expected to support a Biologics License Application (BLA) for nAMD to the FDA next year. RegenxBio is also conducting the Phase II ALTITUDE trial in center-involved DME using the suprachoroidal delivery platform (n=100, NCT04567550). Interim results from the first three cohorts (n=50) showed that 20 percent had a more than two-step improvement in Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scale vs. 10 percent of controls and 54 percent had any DRSS improvement vs. 20 percent of controls.5 Cohort 1 patients got a dose of 1.5 x 1011 gc/eye, which was increased to 5 x 1011 gc/eye in cohorts 2 and 3. None needed prophylactic corticosteroid before or after treatment. The trial is being expanded to include a higher dose of 1 x 1012 gc/eye.
REFERENCES 1. Regillo C. ADVM-022 intravitreal gene therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: End of study results from the 2-year OPTIC trial. Paper presented at the 55th annual Scientific Meeting of the Retina Society; Pasadena, CA; November 4, 2022. 2. Eichenbaum D. Preliminary results from a first-in-human Phase I/II gene therapy trial (FOCUS) of GT005, an investigational AAV2 vector, delivered using the Orbit subretinal system in patients with geography atrophy secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Paper presented at the 55th annual Scientific Meeting of the Retina Society; Pasadena, CA; November 4, 2022. 3. Cohen MN. Phase I study of JNJ-81201877 gene therapy in geographic atrophy (GA) due to age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Paper presented at American Academy of Ophthalmology Retina Subspecialty Day; Chicago, IL; September 30, 2022. 4. Campochiaro PA. Gene therapy for neovascular AMD. Paper presented at American Academy of Ophthalmology Retina Subspecialty Day; Chicago, IL; October 1, 2022. 5. Vajzovic L. Suprachoroidal delivery of RGX-314 for diabetic retinopathy: The Phase II ALTITUDE study. Paper presented at the 55th annual Scientific Meeting of the Retina Society; Pasadena, CA; November 2, 2022. |
Risuteganib (Luminate, Allegro Ophthalmics)
Allegro says it’s preparing a Phase IIb/III clinical trial in patients with intermediate dry AMD. Allegro hasn’t issued an update on results from the Phase IIa trial of risuteganib in nAMD since 2021 (n=40, NCT03626636). Two studies explored how risuteganib may protect retinal pigment epithelium cells.7,8 Risuteganib is a small-peptide oxidative stress stabilizer.
RO7250284 (Genentech/Roche)
The Phase I trial in nAMD, now known as BURGUNDY, is still recruiting patients and enrollment has been raised from 50 to 251 (NCT04567303). RO7250284 is a bispecific human Fab form of faricimab delivered via the port-delivery implant used with Susvimo, the port-delivery implant with ranibizumab. Study completion is set for 2027.
Tarcocimab tedromer/KSI-301 (Kodiak Sciences)
This anti-VEGF biopolymer conjugate is the focus of trials in four indications. The BEACON Phase III trial in RVO (n=568, NCT04592419) met its primary endpoint of noninferiority vs. aflibercept for BCVA change at 24 weeks.
Kodiak also reported completing enrollment in the GLOW Phase III trial of twice-yearly dosing in patients with treatment-naive, moderately severe to severe NPDR without DME (n=253, NCT05066230).
The company also reported what it characterized as disappointing results from the Phase IIb/III DAZZLE flexible-dosing trial in nAMD (n=558, NCT04049266). Topline data showed tarcocimab failed to meet the primary study endpoint of noninferiority vs. aflibercept.
The Phase III DAYLIGHT trial is evaluating monthly tarcocimab in nAMD (n=557, NCT04964089). GLEAM (n=460, NCT04611152) and GLIMMER (n=459, NCT04603937) are evaluating tarcocimab in DME.
THR-149, THR-687 (Oxurion)
An independent data monitoring committee last year advised continuing with the Phase IIb KALAHARI trial in DME (n=126, NCT04527107). The trial is comparing the plasma kallikrein inhibitor THR-149 and aflibercept in anti-VEGF nonresponders. The trial is due for completion by year end, but Oxurion says it expects to report topline data in the second half of the year.
THR-687 is a pan-arginylglycylaspartic acid (RGD) integrin antagonist. Part A dose optimization data from the Phase II INTEGRAL trial in DME (n=16, NCT05063734) failed to meet the key endpoints of improvement in BCVA and CST. Originally slated to enroll 303, Oxurion terminated the trial based on results in 16 patients.
UBX1325 (UNITY Biotechnology)
Unity is pursuing two indications for UBX1325: DME and nAMD. Unity describes UBX1325 as a potent small molecule inhibitor of B-cell lymphoma-extra-large (Bcl-xL) that aims to inhibit the function of proteins that senescent cells rely on for survival.
The Phase II BEHOLD proof-of-concept trial in DME (n=65, NCT04857996) met its 24-week safety and efficacy endpoints, including mean change in BCVA. The company says it expects 48-week safety and efficacy data from the trial in the second quarter. It intends to initiate a pivotal study in DME in the second half of 2023.
In nAMD, the ENVISION Phase II trial completed enrollment (n=46, NCT05275205). Patients are randomized to receive either two doses of UBX1325 (10 mcg) at in the first and fourth weeks or aflibercept (2 mg) every eight weeks. The company expects 16-week safety and efficacy results from ENVISION in the second quarter this year.
Xiflam (InflammX)
Xiflam is an oral, small-molecule NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor that targets the Connexin43 protein and blocks the formation of hemichannels. InflammX last fall submitted an Investigational New Drug amendment that it said at the time would allow the DRCR Retina Network to initiate a Phase IIb trial in DME and DR.
InflammX says the trial will also evaluate the therapeutic effect of Xiflam on biomarkers of active kidney disease. However, no trials have been registered at ClinicalTrials.gov.
Xipere (Clearside Biomedical)
Once known as CLS-TA, Xipere, the suprachoroidal triamcinolone acetonide suspension, already FDA approved for uveitic macular edema, was the subject of the long-completed Phase II TYBEE trial in DME (n=71, NCT03126786). It’s no longer listed in Clearside’s pipeline on its website, but partner Arctic Vision is pursuing the DME indication for a rebranded iteration known as Arcatus/ARVN001 in Australia, New Zealand and Asia. Both companies list a Phase I DME trial in those countries as active.
REFERENCES
1. Bai JY, Wang WY, Dou ZZ, Geng BC, Xu XY, Zhu YZ, Zhao SY, Liu M, Jia SY, Luo WJ. Efficacy of intravitreal conbercept injection on short- and long-term macular edema in branch retinal vein occlusion. Int J Ophthalmol. 2022 18;15:489-494.
2. Zhao T, Chen Y, Zhang HS, Chen Y, Wang ZJ. Efficacy of conbercept after switching from bevacizumab/ranibizumab in eyes of macular edema secondary to central retinal vein occlusion. Int J Ophthalmol. 2022 18;15:609-614.
3. Yang S, Li T, Jia H, et al. Targeting C3b/C4b and VEGF with a bispecific fusion protein optimized for neovascular age-related macular degeneration therapy. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14:eabj2177. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abj2177.
4. Munk M, Bolz M, Strauss, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of ISTH0036, a selective TGF-B2 blocking antisense in preclinical and clinical studies. FP-1050 presented at EURETINA 22; Hamburg, Germany; September 4, 2022.
5. Cheung G. OPT-302 Combination Therapy with Ranibizumab for Treatment of Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy. Paper presented at Bascom Palmer 19th annual Angiogenesis, Exudation, and Degeneration 2022; virtual; February 12, 2022.
6. Dhoot DS. Interim safety and efficacy data from a Phase I clinical trial of sustained-release axitinib hydrogel implant (OTX-TKI) in wet AMD subjects. Paper presented at American Academy of Ophthalmology Retina Subspecialty Day; Chicago, IL; September 30, 2022.
7. Yang P, Trimpey-Warhaftig R, Koo JM, et al. Cellular uptake of risuteganib via endocytosis in cultured human RPE cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022;63:3041.
8. Koo JM, Call C, Zhou D, et al. Risuteganib-directed staining localizes in the retinal pigment epithelium of retinal tissue from aged, but not young mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022;63:4414.
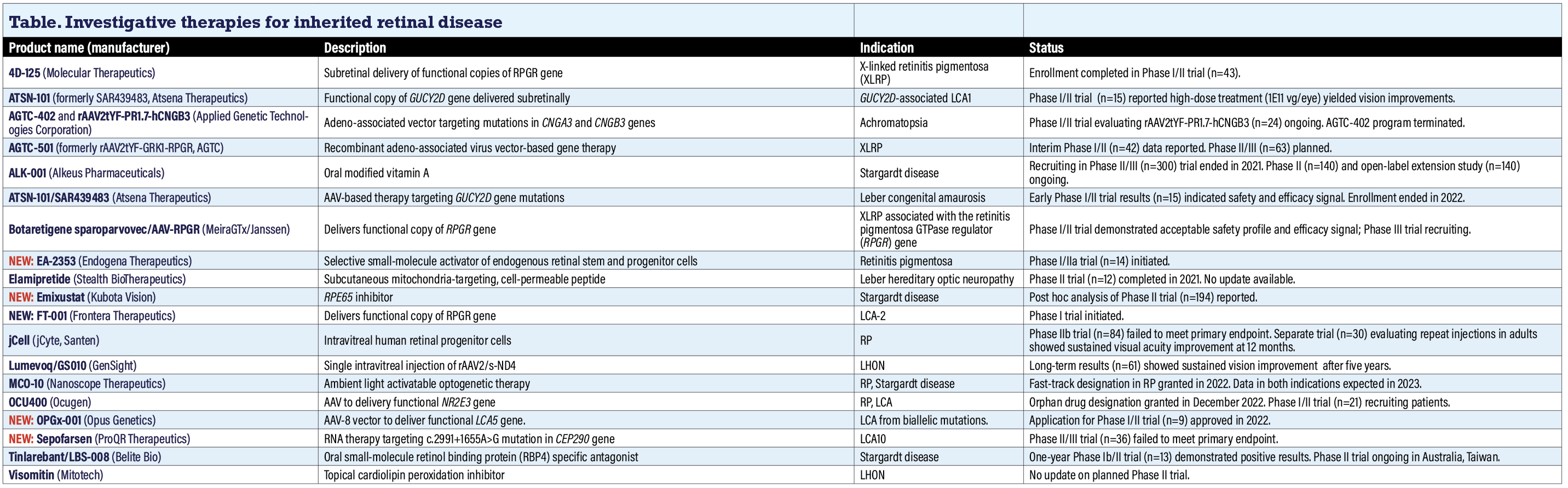
Investigative therapies for inherited retinal disease
4D-125 (Molecular Therapeutics)
The FDA granted Fast Track Designation to 4D-125, which targets inherited retinal dystrophies due to defects in the RPGR gene, including X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP). 4D-125 is designed to deliver a functional copy of the retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator (RPGR) gene to retina photoreceptors. 4DMT completed enrollment in the open-label Phase I/II clinical trial to evaluate the safety of the maximum tolerated dose (n=43, NCT04517149). Secondary endpoints include assessments of both visual function and anatomical endpoints.
Molecular Therapeutics anticipates giving additional updates in 2024. The trial is due for completion in 2029.
AGTC-402, rAAV2tYF-PR.7-hCNGB3, AGTC-501 (Applied Genetic Technologies Corp.)
AGTC is pursuing programs in XLRP and achromatopsia. In achromatopsia, a Phase I/II trial is evaluating the vector rAAV2tYF-PR.7-hCNGB3, targeting the CNGB3 gene (n=32, NTC02599922). A previous program in achromatopsia evaluating AGTC-402 for mutations in the CNGA3 gene was scrapped based on Phase I/II results (NCT02935517).
In XLRP, positive three-month interim data were reported from the ongoing Phase II SKYLINE trial of AGTC-501 (n=42, NCT03316560), a recombinant adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector-based therapy targeting mutations in the RPGR gene. The company says the trial showed robust improvements in visual sensitivity, the trial’s primary efficacy endpoint, in multiple patients three months after dosing, with a 62.5 percent response rate in dose group B and a 25 percent response rate in dose group A. SKYLINE is a multi-site expansion of the ongoing Phase I/II study that’s randomizing patients to either a high or low dose of AGTC-501. A Phase II/III trial evaluating the vector is planned but isn’t yet recruiting (n=63, NCTO4850118). Syncona Ltd. last year acquired AGTC.
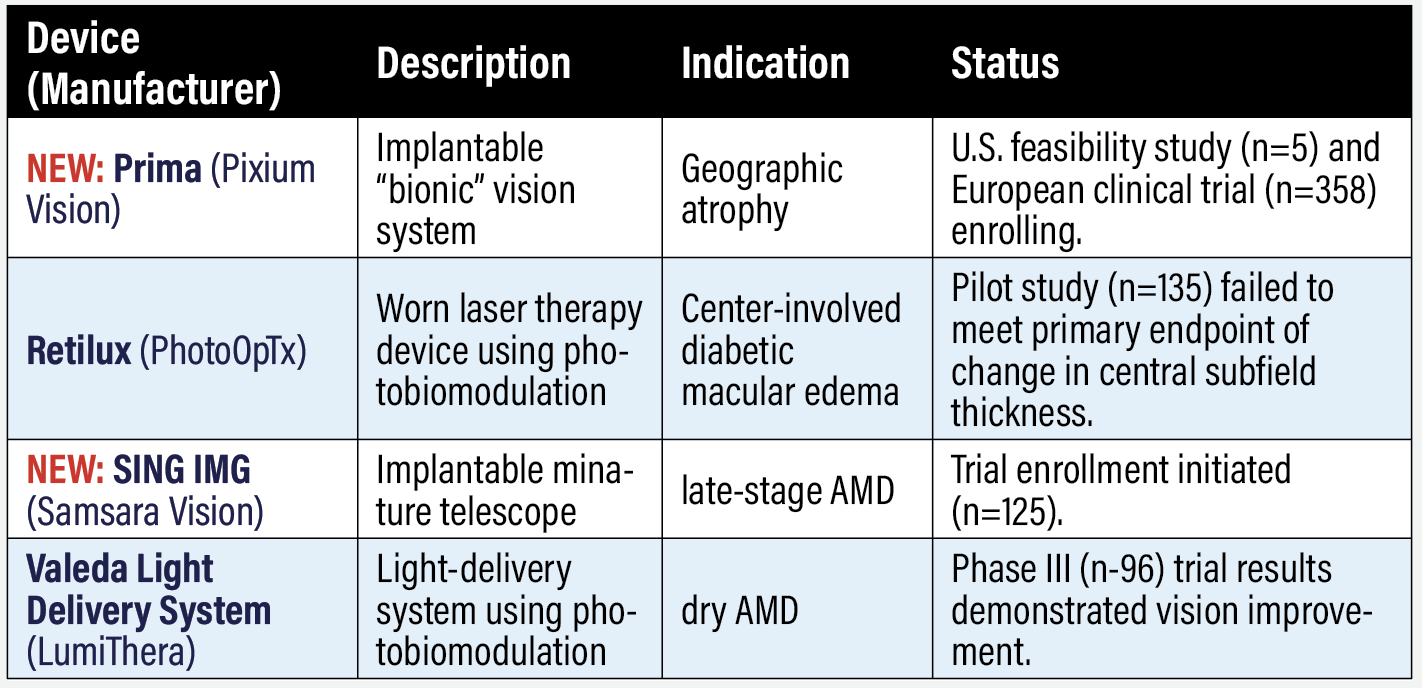
Investigative device-based therapies NEW: Prima (Pixium Vision) This intraocular implant uses a proprietary “bionic” system, as Pixium Vision calls it, to restore vision in geographic atrophy. Enrollment began in 2022 in the PRIMAvera trial (n=358, NCT04676854), with the first successfully completed implantation of a patient in Italy. The trial is scheduled for completion in 2026. Pixium has a second-generation implant that demonstrated improved vision in rats.1 A U.S. feasibility study is also recruiting patients (n=5, NCT03392324), with completion scheduled for year end. Retilux (PhotoOpTx) This device, worn like an eye patch, delivers laser therapy directly to the affected eye using photobiomodulation (PBM), which uses light in the 630-to-900-nm range. The pilot study (n=135, NCT03866473) compared PBM with sham in eyes with center-involved diabetic macular edema and good vision. PBM patients had two daily treatments for 90 seconds at 670 nm for four months. The primary outcome was change in central subfield thickness at four months. Those in the sham group actually had more robust improvement: 15 (standard deviation 57) vs. 13 (53) µm, according to results posted in September 2022 at ClinicalTrials.gov. The company didn’t respond to a request for more information by press time. NEW: SING IMT (Samsara Vision) Samsara started enrollment in the prospective CONCERTO study of this implant in patients with late-stage age-related macular degeneration (n=125, NCT05438732). SING IMT stands for smaller-incision, new-generation, implantable miniature telescope. The first U.S. procedures with the SING IMT were performed last summer. The Food and Drug Administration approved a post-market application supplemental study to evaluate improvements in visual acuity and device safety. CONCERTO is recruiting older adults living with stable, bilateral central scotomas due to late-stage AMD and fovea-involving GA or disciform scar. Valeda Light Delivery System (LumiThera) LumiThera reported findings from the LIGHTSITE III trial in dry AMD (n=96, NCT04065490). Patients were randomized 2:1 to PBM or sham. The trial results demonstrated statistically significant improvement in the prespecified primary endpoint in best-corrected visual acuity at 13 months in the PBM group vs. sham (p =0.02). The PBM arm had a sustained, average increase in Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study letter score of 5.5 letters from baseline at 13 months (p<0.0001). Fifty-five percent of PBM responders demonstrated a >5-letter improvement on the standard EDTRS eye chart with a mean of 9.7 letters and 26 percent achieved a >10-letter improvement with a mean of 12.8 letters.
REFERENCE 1. Wang BY, Chen ZC, Bhuckory M, et al. Electronic photoreceptors enable prosthetic visual acuity matching in the natural resolution in rats. Nature Comm. 2022;13:6627. |
ALK-001 (Alkeus Pharmaceuticals)
Recruiting ended in 2021 in a Phase II/III trial (n=300, NCT03845582) of this oral modified form of vitamin A, but trial results still haven’t been posted. Alkeus is pursuing two trials in Stargardt disease: the Phase II TEASE trial (n=140, NCT02402660), for which completion is scheduled for 2025; and an open-label extension study of TEASE enrolling by invitation only (n=140, NCT 04239625). The trials are evaluating ALK-001 vs. placebo for up to 24 months. ALK-001 is also the subject of a separate trial in geographic atrophy. Alkeus didn’t reply to a query for updated information by press time.
ATSN-101/SAR439483 (Atsena Therapeutics)
ATSN-101, formerly known as SAR439483, is an AAV-based therapy for Leber congenital amaurosis caused by biallelic mutations in the GUCY2D gene. Results from a Phase I/II clinical trial (n=15, NCT03920007) demonstrated that patients tolerated subretinal delivery well with the highest dose of 1 x 1011 vector genes per eye (vg/eye) and had meaningful improvements in vision.1 Trial enrollment ended in July 2022 and study completion is due in 2027.
Botaretigene sparoparvovec/AAV-RPGR (MeiraGTx Holdings/Janssen Pharmaceutical Cos.)
Formerly called AAV-RPGR, this is a recombinant AAV vector designed to deliver functional copies of the RPGR gene in patients with XLRP associated with the RPGR gene. A readout from the ongoing Phase I/II trial (n=49, NCT03252847) demonstrated what Janssen describes as an acceptable safety profile, along with efficacy assessments that showed improvements in retinal sensitivity, visual function and functional vision.2
Three serious adverse events were observed overall. Most were related to the operation to deliver the vector itself and resolved without additional intervention. No dose-limiting events were reported. Janssen reports that a Phase III study is actively dosing patients.
NEW: EA-2353 (Endogena Therapeutics)
Endogena last year initiated a Phase I/IIa trial of EA-2353 in RP (n=14, NCT05392751). Study completion is set for 2025. The company describes the agent as a novel small-molecule candidate that selectively activates endogenous retinal stem and progenitor cells that differentiate into photoreceptors. Endogena also said it would file an Investigative New Drug (IND) application with the FDA for a trial of EA-2351 in GA this year. Endogena didn’t respond to a request for an update by press time.
Elamipretide (Stealth BioTherapeutics)
A Phase II study in Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (n=12, NCT02693119) concluded and reported results in 2021. Two of 16 treated eyes had visual impairment and higher rates of mild ocular surface problems than vehicle. Six treated eyes also had mild cataract, as did five eyes first treated with vehicle before switching to elamipretide. Elamipretide is a cell-permeable peptide that targets mitochondrial dysfunction delivered via a 40-mg subcutaneous injection. Stealth didn’t post an update on the program in 2022 and didn’t respond to an inquiry for an update.
NEW: Emixustat (Kubota Vision)
Emixustat modulates the visual cycle by inhibiting RPE protein 65 (RPE65). Data gathering was completed in the Phase III trial in Stargardt disease in June 2022 (n=194, NCT03772665). A post hoc analysis found that Emixustat treatment resulted in a 40.8 percent reduction in lesion progression compared with placebo at month 24 vs. placebo (p=0.0206, Emixustat n=34, placebo n=21).
NEW: FT-001 (Frontera Therapeutics)
FT-001 is an AAV gene therapy administered by a one-time subretinal injection that aims to deliver a functional copy of the human RPE65 gene to the nuclei of the patient’s retinal cells. Frontera obtained investigational new drug application approvals last year from regulatory authorities in the United States and China and in January initiated a Phase I trial in LCA-2 in China, which isn’t listed at ClinicalTrials.gov. Frontera says it expects a data readout later this year.
 |
| Click image to enlarge. |
jCell (jCyte, Santen)
jCell is an intravitreal injection of human retinal progenitor cells (hRPC) that aims to preserve or potentially restore some vision in RP and related conditions. Results were posted last year from the Phase IIb trial (n=84, NCT03073733) in adults with RP. Patients received either a 3 x 106 or 6 x 106 dose or sham.
The primary trial outcome was average change in best-corrected visual acuity at 12 months. The sham group had an average letter gain of 3.9 (standard deviation 3.9) vs. 1.3 (14.14, p=0.582) and 2.6 (21.53, p=0.984) in the respective dosing groups. However, a higher percentage of treated patients had a VA improvement of ≥13 letters: 11.5, 16 and 30.4 percent for the sham and low- and high-dose groups (p=0.157). A separate trial is evaluating the safety of repeat injections in adults with RP (n=30, NCT04604899).
Lumevoq/GS010 (GenSight Biologics)
In the latest readout of the RESTORE trial of Lumevoq (lenadogene nolparvovec, n=61, NCT03406104), study participants with LHON due to the ND4 mutation continued to show improvement in vision after five years of follow-up. Participants received a single intravitreal injection of rAAV2/2-ND4. RESTORE is the long-term follow-up study of the Phase III RESCUE (n=39, NCT02652767) and REVERSE (n=37, NCT02652780) trials, which demonstrated sustained BCVA improvement in treated patients. GenSight says it anticipates approval in the European Union by the end of the year.
MCO-10 (Nanoscope Therapeutics)
Nanoscope completed enrollment in two trials for its ambient-light activated optogenetic monotherapy: STARLIGHT, a Phase II open-label trial (n=6, NCT05417126) in Stargardt disease; and a Phase IIb/III trial in RP (n=27, NCT04945772).
Six-month data from the Stargardt trial are expected by spring. The FDA granted fast-tack designation for the RP indication last fall. Topline data from the RP trial are expected in the spring.
OCU400 (Ocugen)
OCU400 (AAV-NR2E3) is a modified gene therapy that targets nuclear hormone receptors for RP associated with mutations in the Nr2e3 gene and rhodopsin and LCA with mutations in the Cep290 gene, for which the FDA granted orphan drug designation.
A Phase I/II trial evaluating OCU400 is currently recruiting patients (n=21, NCT05203939). The trial’s drug safety and monitoring board established high-dose OCU400 as the maximum tolerable dose for the dose escalation phase of the study. Enrollment is expected to be completed this year.
NEW: OPGx-001 (Opus Genetics)
The FDA in December 2022 cleared the IND application for a Phase I/II trial in adults with LCA resulting from biallelic mutations in the LCA5 gene (n=9, NCTo5616793). OPGx-001 is an AAV-8 vector designed to precisely deliver a functional LCA5 gene to retinal photoreceptors. It’s administered via subretinal delivery. Animal and human-induced pluripotent stem cell models demonstrated preservation of retinal structure and visual function when OPGx-001 was administered before peak disease activity. The trial is due for completion in 2027.
NEW: Sepofarsen (ProQR Therapeutics)
Sepofarsen is an RNA therapy for LCA10 due to the c.2991+1655A>G mutation in the CEP290 gene. ProQR was conducting a post hoc analysis of 12-month data from the Phase II/III ILLUMINATE trial (n=36, NCT03913143), but sepofarsen failed to meet its primary endpoint of improved BCVA. An open-label, dose-escalation trial of sepofarsen for the same indication in children ages 8 years and younger is listed as recruiting (n=15, NCT0855045). In August 2022 the company said it would focus exclusively on development of its Axiomer RNA-editing technology and seek a strategic partner for its ophthalmology assets, including sepofarsen.
Tinlareband/LBS-008 (Belite Bio)
Belite Bio last year started enrollment in the U.S. Phase III clinical trial of LBS-008, also known as Tinlarebant, in patients with the STGD1 form of Stargardt disease. Interim one-year results of the Phase Ib/II study in adolescent patients with STGD1 (n=13, NCT05266014) demonstrated stabilization of retinal thickness “in many subjects,” Belite Bio reported, along with vision stabilization in nine of 13 patients (69.2 percent).3 Belite Bio also says it’s conducting a two-year Phase II study, which has enrolled 13 subjects at clinical sites in Australia and Taiwan, along with the two-year Phase III trial in adolescent STGD1. Neither is listed at Clinical Trials.gov.
Visomitin/SkQ1 (Mitotech)
Visomitin is a topical cardiolipin peroxidation inhibitor that Mitotech is also developing to treat dry-eye disease and glaucoma. The FDA in 2021 granted orphan drug designation for the treatment of LHON, and Mitotech said last year it was planning to start a Phase II trial for the indication but no trial has been posted at ClinicalTrials.gov. The company didn’t respond to a query for an update by press time. RS
REFERENCES
1. Kay CN. Safety and efficacy of SAR439483 in patients with Leber congenital amaurosis caused by biallelic mutations in GUCY2D (LCA1). Paper presented at the American Academy of Ophthalmology Retina Subspecialty Day; Chicago, IL; October 1, 2022.
2. Michaelides M. Ph 1/2 AAV5-RPGR (botaretigene sparoparvovec) gene therapy trial in RPGR-associate X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP). Paper presented at the American Academy of Ophthalmology Retina Subspecialty Day; Chicago, IL; October 1, 2022.
3. Grigg J. A 2-year Phase Ib/II study of the safety and tolerability of tinlarebant in adolescent STGD1 subjects: Interim findings. Paper presented at the American Academy of Ophthalmology Retina Subspecialty Day; Chicago, IL; October 1, 2022.