 |
Take-home points
|
 |
|
Bios Dr. Finn is an assistant professor of clinical ophthalmology and visual sciences at the Vanderbilt Eye Institute in Nashville, Tennessee. DISCLOSURES: Dr. Finn disclosed relationships with Allergan/AbbVie, Genentech/Roche and Apellis Pharmaceuticals. |
The annual meeting of the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology—ARVO 2022—returned to a live format for the first time since 2019, although some abstracts were presented virtually. More than 11,000 researchers, clinicians and scientists from around the world attended the live meeting in Denver as well as virtual sessions.
Here, we report on four compelling presentations in retina: early results from a Phase I/II trial of a gene therapy that induces complement factor production to target geographic atrophy; a study evaluating a guarded light pipe with a heads-up surgical platform for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment surgery; an analysis of two artificial intelligence algorithms for evaluating retinal fluid in neovascular age-
related macular degeneration; and a study of a personalized treatment interval using faricimab for diabetic macular edema.
Subretinal gene therapy for GA secondary to AMD
 |
The FOCUS trial is evaluating GT005 (Gyroscope Therapeutics), an adeno-associated virus (AAV-2) based gene therapy designed to induce complement factor I production, in geographic atrophy.
Previous clinical trials have shown that complement inhibition slows GA growth. The alternate pathway of the complement system provides several different targets for dry age-related macular degeneration. We have data showing that genes encoding low CFI levels are related to an increased risk of AMD. Serologic data confirms this as CFI supplementation suppresses the complement system alternate pathway and reduces the risk of developing AMD.
By delivering GT005 subretinally, the goal of the FOCUS trial is to allow for long-term CFI expression by creating a biofactory in the eye. This can ultimately downregulate the complement alternate pathway, specifically by sequestering C3b.
Nadia K. Waheed, MD, MPH, an associate professor at Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, presented results from FOCUS, a Phase I/II open label safety and dose-response trial.1 So far, the agent has been well tolerated in the first four cohorts.
Retinal pigment epithelial changes had been noted in the high-dose group. However, these changes were restricted to the bleb area without associated significant visual changes. This side effect has been seen in other subretinal gene therapy trials and may be a reason to administer bleb delivery outside the macula.
 |
Dr. Waheed also said the study found no significant associated immune response and no clinically significant inflammation after GT005 delivery. Vitreous levels of CFI increased as expected after delivery and C3 levels decreased. The hope is that this reduces the chronic inflammatory drive contributing to GA progression.
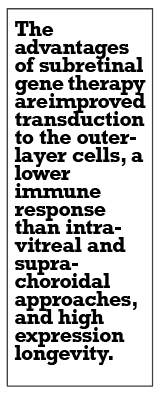
The advantages of subretinal gene therapy for GA are improved transduction to the outer layer cells, lower immune response compared to intravitreal and suprachoroidal approaches, and high expression longevity. The major drawback is that it requires a surgical procedure.
In this vein, a minimally invasive subretinal delivery system, called Orbit, is being designed to deliver subretinal therapy via a suprachoroidal approach. This may improve precision and predictability of delivery and overcome the challenges associated with the traditional surgical-based approach. This delivery system is being tested in cohorts 5 through 7 of the FOCUS study.
Dr. Waheed is chief medical officer of Gyroscope Therapeutics and holds stock in the company. She also disclosed relationships with Nidek, Boehringer Ingelheim, Apellis, Carl Zeiss Meditec, Heidelberg Engineering, Nidek, Optovue, Topcon, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and OcuDyne.
Guarded light pipe in scleral buckling with NGENUITY Platform
 |
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachments are one of the most common surgical diagnoses we as retina specialists treat. We have various techniques to address them, and often scleral buckling is advantageous in young, phakic patients.
John B. Miller, MD, of Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, highlighted the decline in SB procedures, which may be due in part to difficulties with visualization, limited exposure to SB in training and an increasing reliance on widefield visualization both in the clinic with photography and in the operating room.2
Chandelier illumination is one method that addresses some of these challenges, but the illumination and mobility of the chandelier can be limited. Dr. Miller proposed using a guarded light pipe instead, an approach that he said minimizes vitreous movement and dragging.
Guarding the light pipe with a sleeve minimizes its exposure in the vitreous cavity to just the amount necessary to provide adequate illumination. The proposed advantages of combining the guarded light pipe with the three-dimensional heads-up display include improving visualization of the pathology and surgical technique for trainees who may be in the room as well as improving ergonomics for the surgeon. Illumination with the light pipe is used to examine the retina, apply cryotherapy and, in certain cases, drain under direct visualizations. Suturing the sclerotomy the follows this step.
A retrospective case series of eyes repaired with this technique included 31 eyes done with indirect ophthalmoscopy and 16 eyes with the guarded light pipe. The series showed no statistically significant difference in operative times between the techniques, although the guarded light pipe technique trended toward a shorter time.
Surgical outcomes weren’t significantly different between the two study groups. There were no differences in final reattachment rates, visual outcomes, intraoperative complications, reoperation rates or postoperative complications between the two groups. Single-surgery anatomic success was the same at around 87 percent in both groups. One case of vitreous hemorrhage was reported in the guarded light pipe group.
This variation on the traditional SB technique may be advantageous because the light pipe is a familiar tool to vitreoretinal surgeons, costs less than the chandelier, improves the ability to illuminate the peripheral retina and may impart ergonomic and educational benefits.
Dr. Miller is a consultant to Alcon, Allergan/AbbVie, Carl Zeiss, Genentech/Roche and Sunovion.
Retinal fluid volumes as a biomarker for nAMD
 |
Accurate assessment of fluid dynamics on optical coherence tomography is critical for diagnosis, personalized treatment and visual prognosis. This is important for many diseases, including AMD, diabetic macular edema, retinal vein occlusions and central serous chorioretinopathy.
In our current clinical flow and imaging analysis paradigm, we have limitations. These include the time-consuming nature of quantitative analysis and variability between human graders. In a busy clinical environment, we perform binary assessments of whether fluid is present or absent and have limited ability to perform true comparisons of imaging between visits. Artificial intelligence algorithms have the capability to change this by not only detecting fluid, but by segmenting the fluid and color coding it to make it easier to see. Moreover, these algorithms can quantify the fluid so that it may better inform our management decisions.
 |
Tiarnan D.L. Keenan, PhD, of the division of epidemiology and clinical applications at the National Eye Institute, described the application of two AI algorithms to calculate fluid volume for four different neovascular AMD data sets.3 They included clinical trial and real-world data sets: the HARBOR data set, Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 10-year follow-up, and two real-world data sets from Belfast and Tel-Aviv. Fluid volumes in nAMD were quantified including intraretinal fluid compartments, subretinal fluid compartments and pigment epithelial detachments.
The algorithms analyzed more than 20,000 scans from these datasets and made quantitative measures of IRF, SRF and PED volume. This study showed that an AI algorithm can efficiently extract accurate volumes from OCT scans. This type of analysis can have important implications in our clinical practice and research as it may help us to better quantify and follow these imaging biomarkers.
Dr. Keenan has no relevant disclosures.
Personalized treatment interval (PTI) dosing of faricimab for DME
 |
Faricimab (Genentech/Roche) provides dual inhibition of angiopoietin-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor and has the potential to extend treatment durability for DME. YOSEMITE and RHINE were two Phase III, randomized controlled trials in patients with center-involving macular edema.
The personalized treatment interval (PTI) was designed to test the durability of faricimab in these patients. Patients were randomized 1:1:1 into three arms: faricimab q8 weeks; PTI faricimab; and aflibercept q8 weeks.4
The PTI arm received four monthly injections until they achieved central subfield thickness <325 µm, after which the interval could be extended up to q16 weeks based on CST and visual acuity change. The mean vision gains were comparable between the q8-week and PTI faricimab arms. Anatomic results were also favorable. Visual acuity gains were similar to those in the aflibercept q8-week arm. Reductions in CST favored the faricimab arms.
More patients achieved absence of DME and absence of IRF with faricimab. Seventy-nine percent of patients who achieved q12- or q16-week dosing at week 52 remained on q12-week or more dosing without an interval reduction through week 96. Similarly, 76 percent of patients who achieved q16-week dosing at week 52 remained on that interval through week 96. Only 4.7 percent of patients remained on q8-week dosing and 3.9 percent remained on q4-week dosing.
Caroline R. Baumal, MD, of Tufts Medical Center, concluded that PTI dosing in YosemitE and Rhine demonstrated the durability of faricimab in patients with DME. Treat-and-extend-based PTI dosing was able to meet the heterogenous needs of patients with DME.
Most patients in the faricimab PTI arms achieved either q12- or q16-week dosing and these patients were able to maintain this dosing through week 96. The visual acuity gains and anatomic improvements in these patients were similarly maintained over two years. RS
Dr. Baumal disclosed being a consultant to Genentech/Roche, Novartis, Ora, Gemini, Carl Zeiss Meditec and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
REFERENCES
1. Nelson J, MacLaren RE, Heier JS, et al. Preliminary results from a first-in-human Phase I/II gene therapy study (FOCUS) of subretinally delivered GT005, an investigational AAV2 vector, in patients with geographic atrophy secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022;63:1504.
2. Miller J, Sokol J, Ludwig C, Baldwin G. Surgical outcomes of scleral buckling for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment using the NGENUITY three-dimensional visualization system with a guarded light pipe. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022;63:34
3. Keenan T. Fluid dynamics in exudative maculopathies: Prime time for AI to define markers of treatment responsiveness? Paper presented virtually at ARVO 2022; May 12.
4. Baumal CR, Kitchens J, Jaffe G, et al. Personalized treatment interval (PTI) dosing dynamics over 2 years in the Phase 3 YOSEMITE and RHINE trials of faricimab in diabetic macular edema. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022;63;3851



